Code
library(dave.ocpu.client)
source(system.file('app/src/API.R',package='dave.app'))dave.ocpu.client package. All DAVe functionality not listed below can be implemented using the module R libraries directly.library(dave.ocpu.client)
source(system.file('app/src/API.R',package='dave.app'))library(dplyr)
apis <- c(
'dave.ml' = dave_ml_connection,
'ctsgetr' = ctsgetr_connection,
'dave.network' = dave_network_connection,
'dave.path' = dave_path_connection,
'dave.multivariate' = dave_multivariate_connection
)
lapply(1:length(apis), function(i){
status<-apis[[i]]$get()$status_code ==200
data.frame(endpoint=names(apis)[i], status = ifelse(status,'OK','DOWN'))
}) %>%
do.call('rbind',.) endpoint status
1 dave.ml OK
2 ctsgetr OK
3 dave.network OK
4 dave.path OK
5 dave.multivariate OKx<-ocpu_dvmPCA_methods(dave_multivariate_connection)No encoding supplied: defaulting to UTF-8.x$results [1] "svd" "nipals" "rnipals" "bpca" "ppca"
[6] "svdImpute" "robustPca" "nlpca" "llsImpute" "llsImputeAll"library(dave.multivariate.app)
data("dave_data")
data<-dave_databody <- list(
data=data,
pca.components = 2,
pca.cv = 'q2',
pca.algorithm = "svd",
pca.center = TRUE,
pca.scaling = "uv",
seed = 123,
return = "list"
)
x<-ocpu_dvmPCA(dave_multivariate_connection,body=body)
.pca<-x$resultssummary(.pca)$description[1] "Principal components analysis was conducted using the svd method. The data set was centered and scaled using uv. A total of 2 components were calculated, explaining 28.2% variance in the data set. The cross-validated variance explained was 36.1%."data("dave_data_row_meta")
color<-dave_data_row_meta %>% select(class)
label<-dave_data_row_meta %>% select(label)
plot_args<-list(size=5,labels=label,color=color,label=TRUE)# plot_args$type<-'scree'
p<-plot(.pca,plot_args=plot_args,plot_type='scree')
plotly::ggplotly(p)Warning: `gather_()` was deprecated in tidyr 1.2.0.
ℹ Please use `gather()` instead.
ℹ The deprecated feature was likely used in the plotly package.
Please report the issue at <https://github.com/plotly/plotly.R/issues>.plot_args$type<-'cumm'
p<-plot(.pca,plot_type='cumm',plot_args=plot_args) #type not changing
# p<-dave.multivariate.app:::dvmPCA_scree_plot(.pca, type='cumm')
plotly::ggplotly(p)plot_args$type<-NULL
plot_args$point.labels<-plot_args$labels
plot_args$font.size<-3
p<-plot(.pca,plot_type='scores',plot_args=plot_args) #
plotly::ggplotly(p)plot_args$type<-NULL
plot_args$point.labels<-plot_args$labels
plot_args$font.size<-3
p<-plot(.pca,plot_type='diagnostic',plot_args=plot_args) #
plotly::ggplotly(p)data("dave_data_col_meta")
plot_args$color<-NULL
plot_args$point.labels<-dave_data_col_meta$name
plot_args$font.size<-2
p<-plot(.pca,plot_type='loadings',plot_args=plot_args) #
plotly::ggplotly(p)data("dave_data_col_meta")
plot_args$color<-dave_data_row_meta %>% select(class)
plot_args$point.labels<-dave_data_col_meta$name
plot_args$font.size<-2
p<-plot(.pca,plot_type='biplot',plot_args=plot_args) #
plotly::ggplotly(p)library(dave.stat)
library(dave.ml.app)
data("dave_data")
tmp<-dave_data
y<-'class'
.y<-dave_data_row_meta$class
tmp[y]<-.y.metric<-'Kappa'
.method<-c('rf')
classProbs<-TRUE
tuneN<-1
tuneGrid<-NULLbody<-list(data=tmp,y=y)
.data<-ocpu_create_model_data(dave_ml_connection ,body=body)body<-list(method="repeatedcv",num=7,rep=3,classProbs=classProbs) #this need to be flattened to a string
fitControl <- ocpu_create_fit_control(dave_ml_connection ,body=body)# create model
body <-
list(
data = .data,
y = y,
metric = .metric,
method = .method,
fitControl = fitControl,
tuneN = tuneN,
tuneGrid = tuneGrid,
seed= 1234
)
mod<-ocpu_multi_create_predictive_model(dave_ml_connection ,body = body)body<-list(multi_mod=mod)
ocpu_get_model_perf(dave_ml_connection ,body=body)$meta \(meta\)session [1] “x0ab7c097aceeee”
\(meta\)status [1] 201
$paths [1] “/ocpu/tmp/x0ab7c097aceeee/R/.ocpu_get_model_perf” “/ocpu/tmp/x0ab7c097aceeee/R/.val” “/ocpu/tmp/x0ab7c097aceeee/stdout”
[4] “/ocpu/tmp/x0ab7c097aceeee/source” “/ocpu/tmp/x0ab7c097aceeee/console” “/ocpu/tmp/x0ab7c097aceeee/info”
[7] “/ocpu/tmp/x0ab7c097aceeee/files/DESCRIPTION”
$results \(results\)description [1] “Machine learning based predictive modelling was used to predict class. A single model was fit and optimized based on predictive performance on the test data.A random forest model was developed on 51 samples and 188 predictors to predict 2 classes: diabetic.., non.diabetic.. with no pre-processing. Cross validation was done by resampling: cross-validated (7 fold, repeated 3 times) . Tuning parameter ‘mtry’ was held constant at a value of 62.”
\(results\)table model train test metric maximize time_min 1 rf 0.6173153 0.7148289 Kappa TRUE 0.04736702
\(results\)best model train test metric maximize time_min 1 rf 0.6173153 0.7148289 Kappa TRUE 0.04736702 description 1 A random forest model was developed on 51 samples and 188 predictors to predict 2 classes: diabetic.., non.diabetic.. with no pre-processing. Cross validation was done by resampling: cross-validated (7 fold, repeated 3 times) . Tuning parameter ‘mtry’ was held constant at a value of 62.
library(dave.ml.app)
.mod<-get_ocpu_obj(ocpu_session(mod),dave_ml_connection$url)
x<-dave.ml.app::plot.model_list(.mod,type='model',print=FALSE)
ggplotly(x)# see other types c('performance', 'model','importance','confusion','classification')library(dave.ml.app)
.mod<-get_ocpu_obj(ocpu_session(mod),dave_ml_connection$url)
x<-dave.ml.app::plot.model_list(.mod,type='classification',curve='pr',print=FALSE)
ggplotly(x) library(dave.ml.app)
.mod<-get_ocpu_obj(ocpu_session(mod),dave_ml_connection$url)
x<-dave.ml.app::plot.model_list(.mod,type='confusion',percent=FALSE,print=FALSE)
x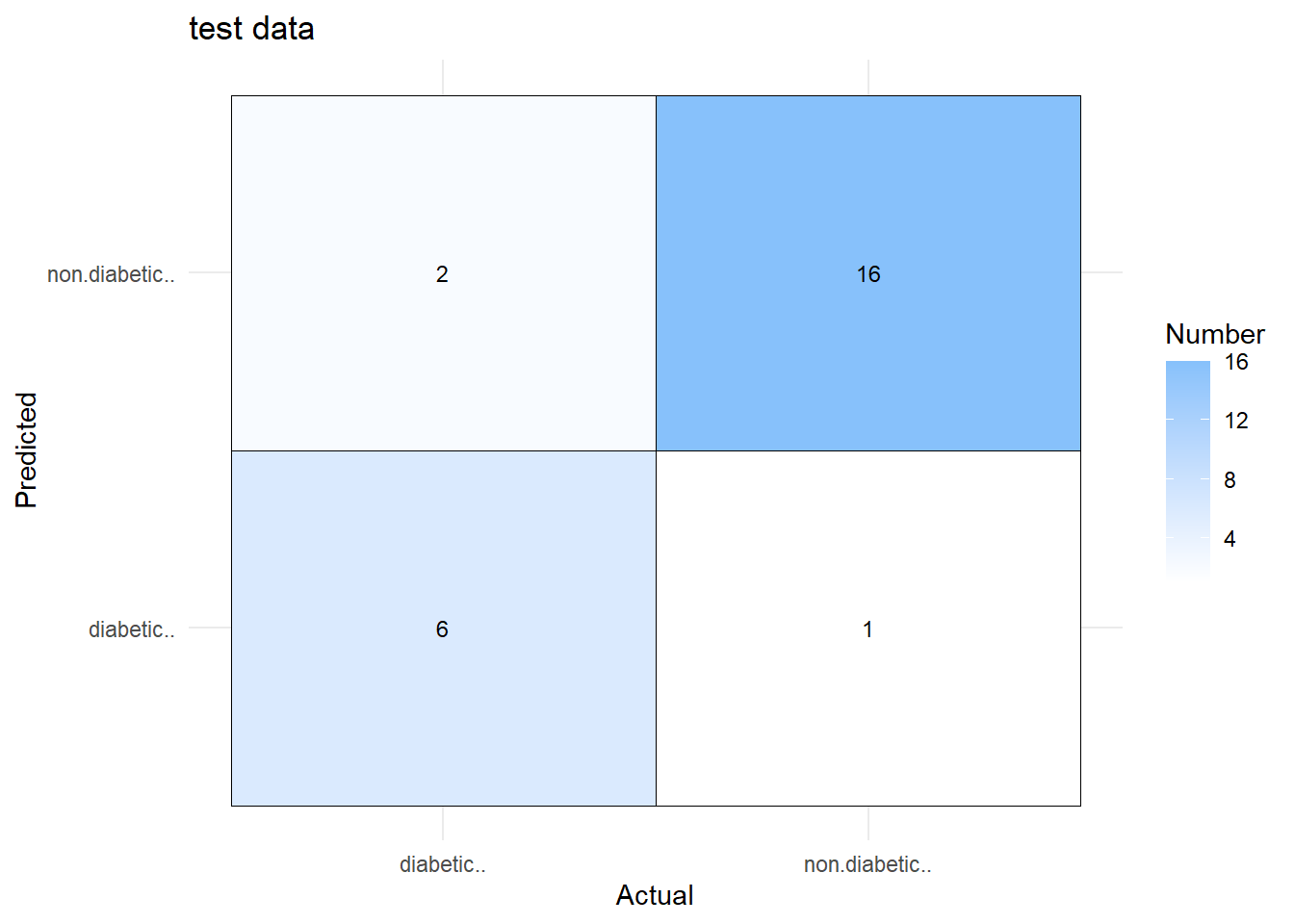
# ggplotly(x) # see other types c('performance', 'model','importance','confusion','classification')RFE to reduce model features (variables) and increase model performance.func<-'rfFuncs' # randomforest
repeats<-1 # repeated CV
number<-5 # CV folds
body<-list(func=func,repeats=repeats,number=number)
ctrl<-ocpu_create_rfe_control(dave_ml_connection ,body) # Increase 'tuneLength' to add more tuning hyperparameter tune grid combinations.
tuneLength<-1
seed<-123
# Specify training data
body<-list(obj=.data,
name='train.data')
train_data<-get_ocpu_list_item(dave_ml_connection ,body)
#specify variable subsets for RFE
#NOTE: referencing previous ocpu session objects dynamically in ocpu calls is not easy. If we need to create a subset for RFE we need to calculate this object in another session and reference its results. To do this we also need to calculate the total number of columns in the `train_data`.
#get total number of columns/features in the data
#encode NULL is used to reference the session. The encoding = 'form' can be used for more complex requirements.
body <- list(x = ocpu_session(train_data))
pkg_url <- 'ocpu/library/base/R/dim'
dims<-ocpu_post(
dave_ml_connection,
body = body,
pkg_url = pkg_url,
encode = NULL,
return_value = TRUE
)$results
#create subset
body <- list(from=1,to=dims[2],by=3)
pkg_url <- 'ocpu/library/base/R/seq'
return_value <- FALSE
.subset<-ocpu_post(
dave_ml_connection,
body = body,
pkg_url = pkg_url,
encode = 'json',
return_value = return_value
)
#carry out RFE feature selection
body <-
list(data = train_data,
y = y,
subset = .subset,
ctrl = ctrl,
tuneLength = tuneLength,
seed = seed)
rfe<-ocpu_create_rfe(dave_ml_connection ,body)#pick subset
best<- 'PickSizeBest' #'pickSizeTolerance' #"PickSizeBest"#'pickSizeTolerance'
metric<-'Kappa'
body<-list(rfRFE=rfe,best=best, metric=metric,tolerance=.1)
# best<- 'pickSizeTolerance'
# tolerance<-5
# body<-list(rfRFE=rfe,best=best,tolerance=tolerance)
#get top model variables
selected_rfe<-ocpu_rebuild_rfe(dave_ml_connection ,body)
.selected_rfe<-get_ocpu_obj(ocpu_session(selected_rfe),dave_ml_connection$url)library(dave.ml.app)
#collect all required args
rfe_select_args<-list(
best_subset = best,
metric = metric,
tolerance = NULL,
func = func
)
do.call('summary.model_rfe',list(c(.selected_rfe,rfe_select_args)))[1] "Recursive feature elimination (RFE) was used to identify top predictive variables. Backward and forward variable selection was done to optimize model Kappa using rfFuncs, validated with for folds repeated times while conducting round(s) of model parameter tuning. The final model was selected based on the best subset method. The selected model contains 16 variable(s) and has Kappa equal to 0.701 +/- 0.163. The top 5 variables include: var188, var173, var51, var15 and var34."x<-dave.ml.app::plot.model_rfe(.selected_rfe,metric = metric,print=FALSE)
ggplotly(x)trans_args<-function(){list(url = "http://ec2-107-21-83-113.compute-1.amazonaws.com:81/ocpu/", body = list(
id = c("C00310", "C00379", "C01762", "C00385", "C00183",
"C02067", "C00299", "C00366", "C00086", "C00106", "C00082",
"C00078", "", "C06771", "C01083", "C01157", "C02477", "C00178",
"C00214", "C00188", "", "", "C00245", "D09007", "C00059",
"C00089", "C00042", "C01530", "C00794", "C08250", "C00493",
"C00065", "C00213", "C00818", "C00199", "C00121", "C00474",
"C00507", "C00022", "C00013", "", "C02457", "C00148", "",
"C00009", "C00346", "", "C00079", "C07086", "C01601", "C00864",
"C08362", "C00249", "C01879", "C00209", "C00295", "C00077",
"C00712", "C02721", "C00253", "C00153", "", "", "C00624",
"", "C00645", "C03136", "", "C02989", "C00073", "", "", "C00208",
"C00149", "C07272", "", "C00047", "C06427", "C01595", "C01725",
"", "C02679 ", "", "C00186", "C00328", "", "C00407", "C00311",
"", "", "C00294", "C02043", "C00954", "C16526", "C00262",
"C00192", "", "C05629", "C00263", "C01817", "C00135", "",
"C00387", "C00160", "C00037", "C00093", "C05401", "C00258",
"C00489", "C00064", "C00025", "C00191", "C00092", "C00031",
"C00257", "", "C00446", "C00124", "C00880", "C01235", "C00122",
"C01018", "C01019", "C00085", "C00095", "C00189", "C00503",
"C08374", "", "C00112", "", "C00097", "C00791", "", "C00327",
"C00158", "C00695", "C00187", "", "C06423", "C01571", "C03044",
"C00099", "C00180", "C08281", "C00049", "C00152", "", "C06425",
"C01904", "C00259", "C00872", "C00026", "C01551", "C00499",
"C00041", "C06104", "C00020", "C00212", "C00417", "C05659",
"", "C01015", "C07588", "C00989", "C00156", "", "C00197",
"", "C01013", "C01089", "", "C06474", "", "C00629", "C02112",
"C00233", "", "C02630", "C05984", "", "", "C00956", "", "D01947",
"", "C01885", "C07326"), from = "KEGG", to = c("KEGG", "InChIKey"
), db_name = "/ctsgetr/inst/ctsgetr.sqlite", from_obj = "KEGG"))}body<-trans_args()$body
x<-ocpu_post(
ctsgetr_connection,
body = body,
pkg_url = 'ocpu/library/CTSgetR/R/CTSgetR',
encode = 'json',
return_value = TRUE
)No encoding supplied: defaulting to UTF-8.head(x$results) id InChIKey KEGG
1 C00310 LQXVFWRQNMEDEE-OVEKKEMJSA-N C00310
2 C00379 HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-SCDXWVJYSA-N C00379
3 C01762 UBORTCNDUKBEOP-UUOKFMHZSA-N C01762
4 C00385 LRFVTYWOQMYALW-UHFFFAOYSA-N C00385
5 C00183 KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-BYPYZUCNSA-N C00183
6 C02067 PTJWIQPHWPFNBW-GBNDHIKLSA-N C02067dave_network_col_meta$id, see dave_network_col_meta to view the corresponding molecule names.library(dave.network.app)
data("dave_network")
data("dave_network_col_meta")
data<-dave_network_col_metaidcolumn<-'CID'
net_index<-'id'
type<-'CID'
DB <- '/open_cpu/CID.SDF.DB'
body<-list(data=data,
idcolumn=idcolumn,
type = type,
net_index = net_index,
DB=DB)
net <- structural_net <-
ocpu_metabolic_network(dave_network_connection, body = body,return_value = TRUE)
lapply(net$results,head)$nodes
ID name KEGG CID id
1 var1 xylulose C00310 5289590 1
2 var2 xylitol C00379 6912 2
3 var3 xanthosine C01762 64959 3
4 var4 xanthine C00385 1188 4
5 var5 valine C00183 6287 5
6 var6 uridine C02067 15047 6
$edges
from to value value.1 type
176 153 27 0.7027027 0.7027027 CID
351 153 74 0.6304348 0.6304348 CID
352 27 74 0.6923077 0.6923077 CID
526 153 39 0.6486486 0.6486486 CID
527 27 39 0.6250000 0.6250000 CID
528 74 39 0.5609756 0.5609756 CID
$node_mapping
NULL
$vis_config
NULLidcolumn<-'KEGG'
net_index<-'id'
type<-'KEGG'
DB <- '/open_cpu/CID.SDF.DB'
body<-list(data=data,
idcolumn=idcolumn,
type = type,
net_index = net_index,
DB=DB)
net <- biochem_net<-
ocpu_metabolic_network(dave_network_connection, body = body)
lapply(net$results,head)$nodes
ID name KEGG CID id
1 var1 xylulose C00310 5289590 1
2 var2 xylitol C00379 6912 2
3 var3 xanthosine C01762 64959 3
4 var4 xanthine C00385 1188 4
5 var5 valine C00183 6287 5
6 var6 uridine C02067 15047 6
$edges
from to value value.1 type
1 1 2 1 1 KEGG
2 1 150 1 1 KEGG
3 4 3 1 1 KEGG
4 36 3 1 1 KEGG
5 103 3 1 1 KEGG
6 95 4 1 1 KEGG
$node_mapping
NULL
$vis_config
NULLlibrary(dave.network.app)
data("dave_network")
tmp_data<-dave_network body <- list(
data = tmp_data,
cor_method = 'spearman',
cor_FDR = TRUE,
cor_cutoff = .05,
lambda = NULL,
huge_method = 'manual'
)
x <-
ocpu_get_cor_mat(dave_network_connection,
body = body)body <-
list(
data = tmp_data,
nlambda = 10,
paranorm = TRUE,
lambda.min.ratio = .1,
check.cor = FALSE
)
huge_obj<-
ocpu_get_huge_obj(dave_network_connection,
body = body,
return_value = TRUE)opt=maual and specify a lambda to manualy tune the network connection strength.body <-
list(
huge_obj=huge_obj,
lambda=NULL, #round(huge_obj$results$lambda[5],4), # legacy shenanigans for manual
opt='stars'
)
huge_edges<-
ocpu_get_huge_edges(dave_network_connection,
body = body)
head(huge_edges$results) source target value
1 2 1 1
2 24 1 1
3 30 1 1
4 36 1 1
5 39 1 1
6 79 1 1#load calculated objects for the network nodes
library(dave.stat)
data("dave_stat_col_meta")
#join external analysis results with a calculated network
network_obj <- biochem_net$results
#match internal indicies
dave_stat_col_meta$id <- gsub('var', '', dave_stat_col_meta$ID)
network_obj$nodes <-
left_join(network_obj$nodes, dave_stat_col_meta, by = 'id')
#create mappings for node attributes
FC <-
map_fold_change(network_obj$nodes$FC_non.diabetic.._diabetic.., transform = 'log2')$results
FC$'_dir' <- factor(FC$'_dir',labels = c('increased','unchanged','decreased'),levels = c(1,0,-1))
network_obj$nodes <- cbind(network_obj$nodes, FC = FC)
network_obj$node_mapping <- list(
node_col = 'FC._dir',
node_size = 'FC._mag',
node_label = 'name.y',
node_size_range = c(3, 7)
)
x <- do.call('network.visualize', network_obj)
# network.visnetwork(x)
ggplotly(dave.network.app:::plot.network_viz(x))library(dave.ocpu.client)
source(system.file('app/src/API.R',package='dave.app'))DAVe API endpoints only require a body argument and you can see all the created asset paths by setting return_value = FALSE.data("mtcars")
body<-list(x=mtcars)
pkg_url <- 'ocpu/library/base/R/colnames' #this will call base::colnames
res0<-ocpu_post(
dave_ml_connection,
body = body,
pkg_url = pkg_url,
encode = 'json',
return_value = TRUE
)$results
res0 [1] "mpg" "cyl" "disp" "hp" "drat" "wt" "qsec" "vs" "am" "gear" "carb"res1<-ocpu_post(
dave_ml_connection,
body = body,
pkg_url = pkg_url,
encode = 'json',
return_value = FALSE
)
cat('Add the "$paths" below to the following url to view the results:')Add the "$paths" below to the following url to view the results:cat(dave_ml_connection$url)http://ec2-52-22-43-130.compute-1.amazonaws.com/ml/res1$meta
$meta$session
[1] "x059dd61ae4576c"
$meta$status
[1] 201
$paths
[1] "/ocpu/tmp/x059dd61ae4576c/R/.val" "/ocpu/tmp/x059dd61ae4576c/R/colnames" "/ocpu/tmp/x059dd61ae4576c/R/x" "/ocpu/tmp/x059dd61ae4576c/stdout"
[5] "/ocpu/tmp/x059dd61ae4576c/source" "/ocpu/tmp/x059dd61ae4576c/console" "/ocpu/tmp/x059dd61ae4576c/info" "/ocpu/tmp/x059dd61ae4576c/files/DESCRIPTION"get_ocpu_obj(ocpu_session(res1) ,dave_ml_connection$url) [1] "mpg" "cyl" "disp" "hp" "drat" "wt" "qsec" "vs" "am" "gear" "carb"body<-list(x=res1, collapse='|')
pkg_url <- 'ocpu/library/base/R/paste'
ocpu_post(
dave_ml_connection,
body = body,
pkg_url = pkg_url,
encode = 'form',
return_value = TRUE
) $results[1] "mpg|cyl|disp|hp|drat|wt|qsec|vs|am|gear|carb"ocpuclient::get_ocpu_list_item is useful for selecting specific named list elements from previous sessions results.#get a specific element from a previous session either by list index or name
body<-list(obj='<NAME of OBJECT>',
name='<NAME of LIST ITEM>')
get_ocpu_list_item(dave_ml_connection ,body)